Our Services
High quality neurological care with a comprehensive patient centered approach
We provide a wide variety of neurological consultation for the following conditions
- ALS/Lou Gehrig's disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- Back pain
- Bell's palsy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Chronic Migraine
- Concussion/Brain injury
- Dementia
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Hemifacial spasm
- Memory loss
- Memory Impairment
- Movement disorders
- Multiple sclerosis(MS)
- Muscle disease
- Muscular dystrophy
- Nerve injuries/numbness
- Nerve/Spinal pain
- Neuropathy
- Parkinson's disease
- Seizures(epilepsy)
- Stroke
- Tremor
- Vertigo
- Weakness
Services
- Neurological Consultation
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- Botox®
- Independent Medical Examiner
Neurological Consultation

Neurological Consultation is a face-to-face evaluation with the neurologist in which your neurological history is obtained. In addition, a physical exam will be performed for assessing your condition. Post evaluation, the neurologist will consider further diagnostics and management options.
Preparation
- Bring all relevant records, including prior neurological consultation notes or letters, reports of radiological tests (such as X-rays, CT scans or MRI scans), electrodiagnostic studies (such EEG or EMG) and blood tests, and films of CT or MRI scans, if possible, for the appointment for the neurologist to review.
- Bring a list of your current medications, including doses.
- Bring the name, address and fax number of the referring physician so that a consultation note can be sent to the physician.
- Plan on spending up to an hour or longer at the clinic from the time of the appointment.
Electromyography
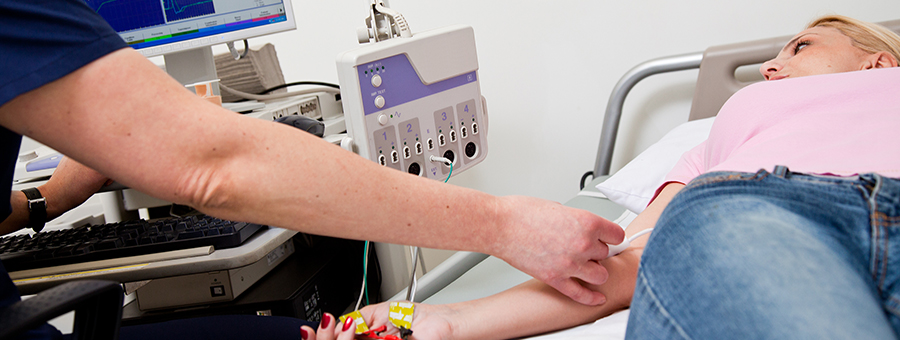
Electromyography (EMG) is a procedure for assessing the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using a computerized electromyograph which detects the electrical potential generated by muscle cells when neurologically activated. EMG can detect nerve and muscle dysfunction.
Why is it done?
This test is done to diagnose/ rule out the following conditions:
- Muscle disorders such as statin myopathy, muscular dystrophy, polymyositis
- Nerve disorders such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Peripheral nerve entrapments such as carpal tunnel syndrome and ulnar neuropathy
- Neuromuscular junction disorders such as myasthenia gravis
- Disorders of motor neurons such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gehrig's disease
- Disorders that affect the nerve root (a.k.a. pinched nerves) caused by nerve injury or damage
How is it done?
EMG uses electrodes to transmit or detect electrical signals. A needle electrode is inserted directly into a muscle and the electrical activity of the muscle is recorded. An EMG translates this electrical activity into signals, graphs and sounds that the neurologist interprets.
Preparation
- Usage of lotions and oils should be avoided a few days before and specifically on the day of the test.
- The doctor should be notified if you are taking any blood thinners such as Coumadin, Plavix or Aspirin.
- Your doctor may request other specific preparation based on your medical condition.
Nerve Conduction Studies
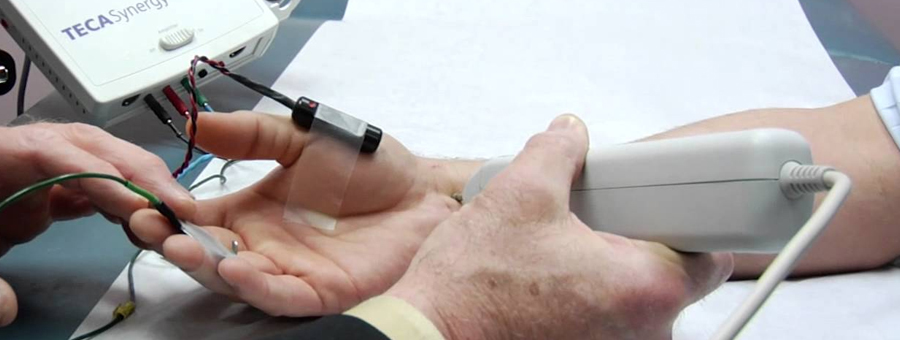
Nerve Conduction Studies also known as Nerve Conduction Velocity Test is done to measure the speed of conduction of electrical signals through a nerve. This test helps in diagnosing nerve destruction and damage.
Why is it done?
Nerve Conduction Study is usually done along with Electromyography in order to differentiate between a nerve disorder and a muscle disorder. This test helps evaluate diseases such as:
- Myopathy
- Myasthenia gravis
- Lambert - Eaton Syndrome
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Herniated disk disease
- Sciatic nerve problems
How is it done?
In this test, surface electrodes are placed on the skin to stimulate the nerve. One electrode gives off a mild electrical impulse while another electrode records it. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by other electrodes. The speed of the nerve signals is measured with the distance between the electrodes and the time taken for the electrical impulses to travel between the electrodes.
Preparation
- The procedure will be explained in further detail by the neurologist.
- Fasting or sedation is not required.
- The doctor should be notified if you are taking blood thinners such as Coumadin, Aspirin or Plavix.
- Avoid using lotions and oils on the day of the exam.
Electroencephalography
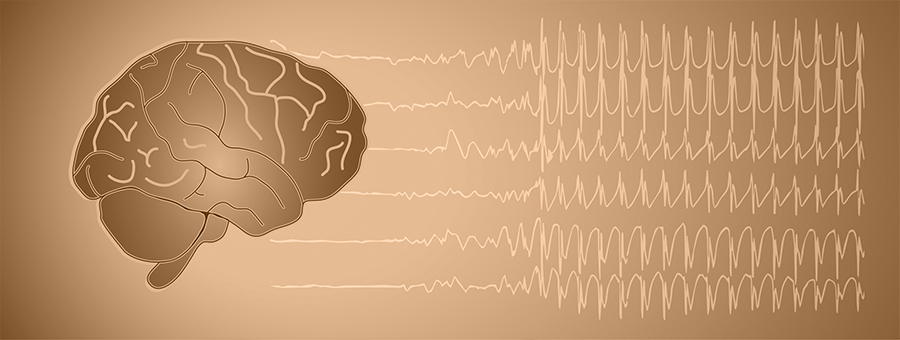
Electroencephalography is a test to measure and record the electrical activity of the brain. This test is used for evaluating brain disorders.
Why is it done?
Electroencephalography helps in diagnosing the following conditions:
- Epilepsy and the types of seizures
- Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- Sleep disorders such as Narcolepsy
- Head injuries, confusion or fainting spells
- Brain activity during a surgery or when a person is in coma
- Tumors or periods of memory loss
- Brain dysfunctions (encephalopathy)
- Stroke, inflammation of the brain
How is it done?
Several metal discs (electrodes) are placed all over the scalp and held in position using a paste. The electrodes are connected with the help of wires to a recording machine. This machine records the electrical activity of the brain. The electrical activity is represented as wavy lines on an EEG recording.
You would be asked to lay still during the test. You may also be asked to do certain other things like breathing rapidly or look at a bright flashing light or may be asked to sleep. If the brain activity needs to be recorded for longer, an ambulatory EEG may be ordered, where a special recorder will also be carried by you in addition to the electrodes. This way the electrical activity of the brain can be recorded for up to three days while you go on about your routine activities.
Preparation
- The procedure will be explained to you by your doctor and you can ask any questions during this time.
- Avoid caffeine on the day of the test.
- Wash your hair a day before the test but don't use any conditioners, styling gels or creams.
- Dress in clothes that are permitted in the testing area.
- Fasting or sedation is generally not required.
BOTOX®
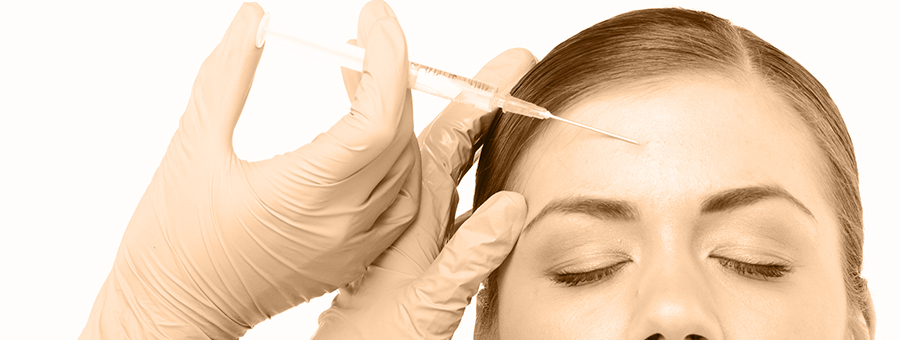
BOTOX®, a drug made from a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum is used in small doses to treat certain conditions.
Why is it done?
BOTOX® performed at Synapse Neurology is used to treat the following conditions:
- Chronic migraine/headache http://www.botoxchronicmigraine.com/
- Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS)- stiffness/contracture of the arm that occurs secondarily to a stroke, brain injury or birth related injury http://hcp.botoxmedical.com/UpperLimbSpasticity
- Cervical dystonia - a neurological disorder that causes severe neck and shoulder muscle contractions. http://www.botoxcervicaldystonia.com
How is it done?
The portion of the body to be treated is prepared with alcohol swabs. The area is then injected with Botox® using micro needles. The injections feel like pinpricks and some other mild discomfort may also be experienced.
Preparation
- Inform your doctor if you've received any type of botulinum toxin injections within the past four months.
- Inform your doctor if you're taking any muscle relaxants, sleeping aids or allergy medications.
- You may be asked to stop taking blood thinners for several days before your injection to avoid the risks of bleeding and bruising.
- Further risks and warnings are discussed at the website links demarcated at each of the specific websites under conditions treated.
Independent Medical Examiner

Dr.Sambandam performs Independent Medical Examinations (IMEs) and provides expert reports regarding injuries, impairments and disabilities. He performs IMEs at the request of both plaintiff and defense attorneys, insurance companies, government agencies and other entities.